Statistics
At June 30 2021 there were 2,402,254 actively trading businesses in the Australian economy.
In 2020-21 there was a:
- 3.8%, or 87,806, increase in the number of businesses.
- 15.8% entry rate, with 365,480 entries.
- 12.0% exit rate, with 277,674 exits.
Information on quarterly experimental counts of Australian businesses for the 5 quarters ending June 2021 can be found below and in the associated data cube.

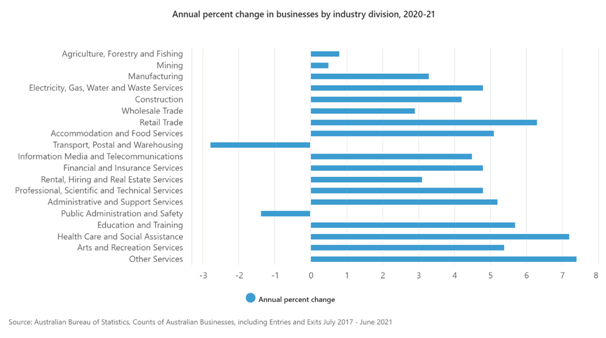
In 2020-21 the three industries with the largest net increase in businesses were:
- Construction (an increase of 16,603 to 410,839 businesses)
- Professional, Scientific and Technical services (an increase of 14,432 to 316,462 businesses)
- Health Care and Social Assistance (an increase of 10,674 to 159,076 businesses)
The three industries with the largest percentage growth in businesses in 2020-21 were:
- Other Services (+7.4%, with an increase of 7,868 to 114,575 total)
- Health Care and Social Assistance (+7.2%, with an increase of 10,674 to 159,076 total)
- Retail Trade (+6.3%, with an increase of 8,593 to 145,079 total)
The industry with the largest percentage decrease in businesses in 2020-21 was:
- Transport, Postal and Warehousing (-2.8%, with an decrease of 5,589 to 194,459 total)
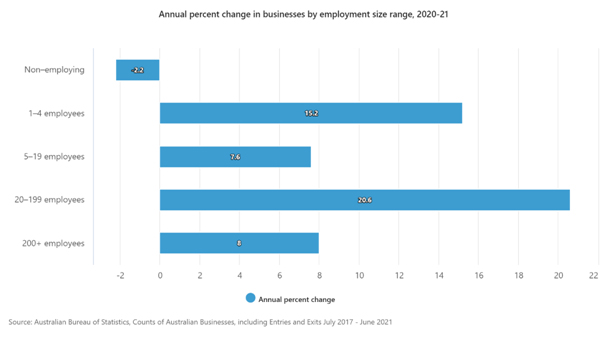
In 2020-21 the number of employing businesses increased by 13.6%, with a net movement of 58,209 surviving businesses from non-employing to employing. There was a:
- 15.2% increase in businesses with 1-4 employees, increasing by 92,495 to 699,623 total.
- 7.6% increase in businesses with 5-19 employees, increasing by 16,198 to 230,633 total.
- 2.2% decrease in non-employing businesses, decreasing by 31,056 to 1,410,049 total.
Business ability to meet financial commitments over the next three months, by top industries

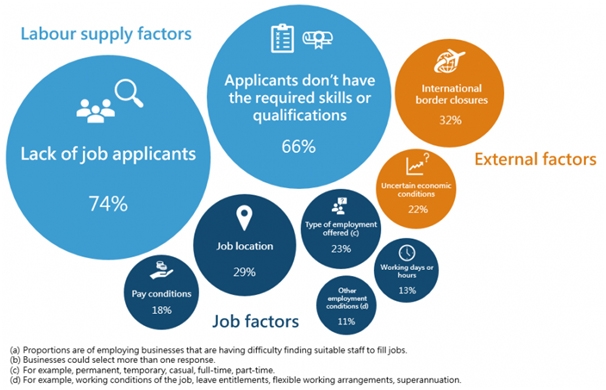
Staff shortages
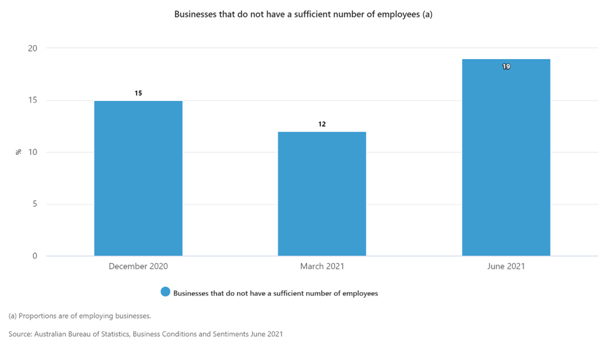
In June, 19% of employing businesses reported that they did not have enough employees based on current operations, compared to 12% in March 2021 and 15% in December 2020. Businesses in Construction (29%) and Retail trade (27%) were the most likely to report staff shortages.
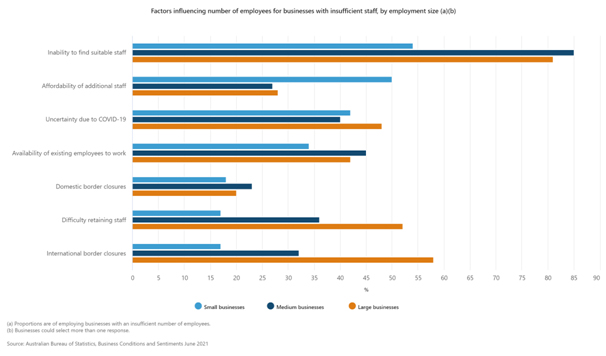
Factors influencing businesses with staff shortages
The 19% of businesses that had an insufficient number of employees reported on factors that were influencing the number of staff they had. The most common factors reported by these businesses were:
- inability to find suitable staff (57%);
- affordability of additional staff (48%);
- uncertainty due to COVID-19 (42%);
- availability of existing employees to work (34%);
- domestic border closures (19%);
- difficulty retaining staff (19%); and
- international border closures (18%).